The Year and The Seasons
Dictionary Definitions
Seasons
- the seasons are the main periods into which a year can be divided and which each have their own typical weather conditions
- season can be used to refer to the period during each year when a perticular activity or event takes place
- season can be used to refer to the period when a particular fruit, vegetable or other food is ready for eating and is widely available
- each of the four divisions of the year (spring, summer,autumn and winter) marked by a particular weather pattern and daylight hours, resulting from the earths changing position with regard to the sun,
- a period of the year characterized by a particular climatic feature or marked by a particular activity, event or festivity.
- a proper and suitable time
- an indefinite or unspecified period of time; a while
- the period of 365 days (or 366 days in a leap yer) starting from the first of January, used for reckoning time in ordinary circumstances
- a period of twelve months measured from a point other than the 1st of January
- a year regarded in terms of the quality of something produced
- a period similar to a year used for reckoning time according to other calendars
- ones age or time of life
- a very long time, ages
- a period of 365 or 366 days, in the Gregorian calendar, divided into 12 calendar months, starting on Jan 1st and ending 31st Dec
- a period of approximately the same length in other calendars
- a space of 12 calendar months calculated from any point
- the time in which any planet completes a revolution round the sun
- a full round of the seasons
- a period out of every 12 months, devoted to a certain pursuit, activity, or the like
- the season after winter and before summer, in which vegetation begins to appear, in the northern hemisphere from March to May and in the southern hemisphere from September to November
- short for spring tide
- originate or arise from
- to come into being, rise, or arise within a short time (usually followed by up)
- to come into being by growth, as from a seed or germ, bulb, root etc; grow, as plants
The year is divided into four seasons spring, summer, autumn or winter.
Each season lasts about three months because there are twelve months within the year.
The dates of the seasons are defined using either the astronomical definition and meteorological definition.
The astronomical definition uses the equinox and solstice dates to indicate the start and finish of the seasons.
In the astronomical seasons:
- spring starts on the spring equinox
- summer starts on the summer solstice
- autumn begins on the autumn equinox
- winter starts on the winter solstice
The equinoxes and solstices change every year so the seasons do also.
The dates for the solstices and equinoxes for this year and next are listed above.
The meteorological seasons start on the first day of the month of the equinox and solstices.
These start on:
- March 1st to May 31st is spring
- June 1st to August 31 is summer
- September 1st to November 30th is autumn
- December 1st to February 28th or 29th is winter
Seasons are opposite to those in the southern hemisphere.
- either of the two time in the year, the summer solstice and the winter solstice, when the sun reaches its highest or lowest point in the sky at noon, marked by the longest and shortest days
- a furthest or culminating point
- the time or date (twice each year) at which the sun crosses the celestial equator, when day and night are of equal length
- the time when the sun crosses the plane of the Earths equator, making night and day approximately equal length all over the earth
- either of the equinoctial points
- pertaining to the celestial equator
The celestial equator runs through the celestial sphere exactly half way between the two poles.
Varying degrees of solar radiation / sunlight reach different parts of the Earth creating different seasons across the globe.
The Earth has an axis through the center of it from the North to South poles.
When the northern hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun it is Summer in the UK.
The highest temperatures are seen around London whilst Scotland and Northern England are the coolest.
Temperatures increase causing heat waves and sometimes droughts.
Plants grow and mature during the summer.
During autumn the leaves change colour due to falling temperatures in autumn.
Temperatures drop, nights are longer and unsettled weather occurs.
Plants start to go dormant.
Animals start storing food for the winter or migrate.
Harvesting occurs at this time.
Winters often have unsettled and windy weather.
The earths axis is tilted furthest away from the sun in winter meaning less light and warmth hits the northern hemishpere.
In winter the days are the shortest and the nights are the longest.
Snow and ice are common in winter, it also becomes colder and wetter.
Using the images found on the internet colour swatches from each of the seasons within all of the images were collected. This will allow common colours for each season to be picked out which could then be matched to the Colourplan papers.
The winter palette has a mix of white and greys which are found within snow and frost seen in winter. The blues and purples reflect the sky within this season. Overall the colour palette is mostly very subtle with a mix of neutral and cold colours.
A year in Earth is how long it takes to complete one orbit around the Sun.
A complete orbit takes 365 days there are 366 days in a leap year.
There are 12 months in a year.
Each of the months have the following amount of days within them:
http://www.22facts.com/spring/
https://www.metoffice.gov.uk/learning/seasons
https://greenwichmeantime.com/longest-day/equinox-solstice-2010-2019/
https://www.timeanddate.com/calendar/aboutseasons.htmlv
https://www.livescience.com/25202-seasons.html
https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/seasons/en/
https://www.britannica.com/science/spring-season
http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/environment_earth_universe/astronomy_space/revision/5/
https://www.britannica.com/science/celestial-equator
- each of the four divisions of the year (spring, summer,autumn and winter) marked by a particular weather pattern and daylight hours, resulting from the earths changing position with regard to the sun,
- a period of the year characterized by a particular climatic feature or marked by a particular activity, event or festivity.
- a proper and suitable time
- an indefinite or unspecified period of time; a while
Year
- the time taken by the Earth to make one revolution around the Sun- the period of 365 days (or 366 days in a leap yer) starting from the first of January, used for reckoning time in ordinary circumstances
- a period of twelve months measured from a point other than the 1st of January
- a year regarded in terms of the quality of something produced
- a period similar to a year used for reckoning time according to other calendars
- ones age or time of life
- a very long time, ages
- a period of 365 or 366 days, in the Gregorian calendar, divided into 12 calendar months, starting on Jan 1st and ending 31st Dec
- a period of approximately the same length in other calendars
- a space of 12 calendar months calculated from any point
- the time in which any planet completes a revolution round the sun
- a full round of the seasons
- a period out of every 12 months, devoted to a certain pursuit, activity, or the like
Spring
- the season after winter and before summer, in which vegetation begins to appear, in the northern hemisphere from March to May and in the southern hemisphere from September to November- short for spring tide
- originate or arise from
- to come into being, rise, or arise within a short time (usually followed by up)
- to come into being by growth, as from a seed or germ, bulb, root etc; grow, as plants
Summer
- the warmest season of the year, in the northern hemisphere from June to August and in the southern hemisphere from December to February
- the period from the summer solstice to the autumnal equinox
- years, especially of a persons age
- the season between spring and autumn , in the Northern Hemisphere from the summer solstice to the autumnal equinox, and in the Southern Hemisphere from the winter solstice to the vernal equinox.
- a period of hot, usually sunny weather
- the hotter half of the year (opposed to winter)
- having the weather or warmth of summer
- the period of finest development, perfection, or beauty previous to any decline
Autumn
- the season after summer and before winter, in the northern hemisphere from September to November and in the southern hemisphere from March to May
- a period from the autumn equinox to the winter solstice
- a time of full maturity, especially the late stages of full maturity or , sometimes, the early stages of decline
- the season between summer and winter; fall. In the Northern Hemisphere it is from September equinox to the December solstice; in the Southern Hemisphere it is from the March equinox to the June solstice.
Winter
- the coldest season of the year in the northern hemisphere from December to February and in the southern hemisphere from June to August
- the period from the winter solstice to the vernal equinox
- (of fruit) ripening late in year
- (of wheat or other crops) sown in autumn for harvesting the following year
- (especially of a bird) spend the inter in a particular place
- cold weather
- the colder half of the year
When do the seasons start?
The year is divided into four seasons spring, summer, autumn or winter.
Each season lasts about three months because there are twelve months within the year.
The dates of the seasons are defined using either the astronomical definition and meteorological definition.
The astronomical definition uses the equinox and solstice dates to indicate the start and finish of the seasons.
In the astronomical seasons:
- spring starts on the spring equinox
- summer starts on the summer solstice
- autumn begins on the autumn equinox
- winter starts on the winter solstice
The equinoxes and solstices change every year so the seasons do also.
The dates for the solstices and equinoxes for this year and next are listed above.
The meteorological seasons start on the first day of the month of the equinox and solstices.
These start on:
- March 1st to May 31st is spring
- June 1st to August 31 is summer
- September 1st to November 30th is autumn
- December 1st to February 28th or 29th is winter
Seasons are opposite to those in the southern hemisphere.
Define Solstice
- either of the two time in the year, the summer solstice and the winter solstice, when the sun reaches its highest or lowest point in the sky at noon, marked by the longest and shortest days - a furthest or culminating point
Define Equinox
- the time or date (twice each year) at which the sun crosses the celestial equator, when day and night are of equal length- the time when the sun crosses the plane of the Earths equator, making night and day approximately equal length all over the earth
- either of the equinoctial points
Define Equinoctial
- pertaining to an equinox or the equinoxes, or to the equality of day and night- pertaining to the celestial equator
The celestial equator runs through the celestial sphere exactly half way between the two poles.
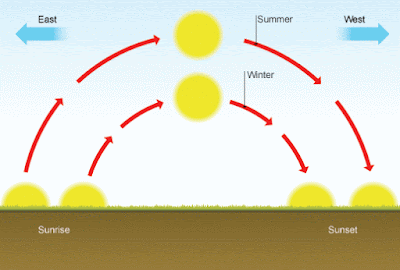
Why do the seasons occur?
There is a 23.5 degree tilt to the Earths rotational axis meaning parts of the Earth are tilted towards the Sun at different points during the year.Varying degrees of solar radiation / sunlight reach different parts of the Earth creating different seasons across the globe.
The Earth has an axis through the center of it from the North to South poles.
When the northern hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun it is Summer in the UK.
The tilt in the Earths axis means that the Sun is higher in the sky during Summer, when we are tilted towards it, whereas in winter the sun is lower because we are tilted away.
Spring
Spring is one of the most recognizable seasons as days become longer and temperatures are warmer.
Plants begin to grow and blossom occurs on trees, whilst animals come out of hibernation.
Vernal from the vernal equinox comes from the latin 'vernus' which means bloom.
Weather in spring is usually calm and dry because the Atlantic loses heat in Autumn and Winter meaning less heat and moisture is transferred to the atmosphere. Temperatures can rise during the day because the sun is high but are cool at night.
The season is associated with rebirth, renewal and regrowth.
Flowers emerge, birds start building nests.
Temperatures rise and the days are longer.
Seeds begin to root and plants grow.
the weather is warmer and wetter.
Animals wake up from hibernation or come back from thier migration.
The season is associated with rebirth, renewal and regrowth.
Flowers emerge, birds start building nests.
Temperatures rise and the days are longer.
Seeds begin to root and plants grow.
the weather is warmer and wetter.
Animals wake up from hibernation or come back from thier migration.
Summer
Summer is the warmest and sunniest season although rainfall varies.The highest temperatures are seen around London whilst Scotland and Northern England are the coolest.
Temperatures increase causing heat waves and sometimes droughts.
Plants grow and mature during the summer.
Autumn
During autumn the leaves change colour due to falling temperatures in autumn.Temperatures drop, nights are longer and unsettled weather occurs.
Plants start to go dormant.
Animals start storing food for the winter or migrate.
Harvesting occurs at this time.
Winter
In this season some animals hibernate or migrate to avoid the cold weather.Winters often have unsettled and windy weather.
The earths axis is tilted furthest away from the sun in winter meaning less light and warmth hits the northern hemishpere.
In winter the days are the shortest and the nights are the longest.
Snow and ice are common in winter, it also becomes colder and wetter.
Existing images relating to seasons
When searching the seasons in google much of the imagery within the results visualises the seasons as a quartet of images allowing for comparison between images and showing the progression from one season to the next.
Within the images there is a clear difference in colour between the different seasons with the vector art using certain colours to represent each of the seasons and the photographic images showing changes of tones throughout the year.
Many of the images focus around the change in nature through the seasons, specifically using trees which see the greatest physical change throughout the year, from blossom to falling of leaves.
In the spring images there is a focus on new growth of leaves and blossom, whilst summer focuses on blue skies, green foliage, warmth and sun. Autumn revolves around the changing of leaves to red and orange whilst leaves start to fall. Winter is shown through snow, trees with no leaves and grey skies.
Many of the images also show the same scene throughout the year from the same vantage point to allow the difference within the pictures to be shown.
Colour swatches from images
Common colours within spring images are a mix of light and dark greens showing the new growth. Pastel pinks and light yellows represent the blossom on the trees. Blues represent the clear skies within spring. Overall the colour scheme uses quite a few muted pastel colours when compared with the other seasons.
In the summer palette the greens and blues are much brighter reflecting how everything is reaching maturity and the weather is much clearer whilst the oranges and yellows represent the warmth and sun that comes with summer.
The autumn palette uses lots of burnt oranges, red and brown reflecting the changing of leaves and creating a warm colour palette.
A Year
A year in Earth is how long it takes to complete one orbit around the Sun.
A complete orbit takes 365 days there are 366 days in a leap year.
There are 12 months in a year.
Each of the months have the following amount of days within them:
There are 52 weeks in a year (average 52. 1429 weeks).
There are 8760 hours in a year or 525600 minutes.
In a month there is 43800 minutes, 730.001 hours, 30.4167 days on average or 4.34524 weeks (average).
There are 7 days in a week, 168 hours, 10080 minutes or 604800 seconds in a week.
There are 24 hours in a day, 1440 minutes or 86400 seconds in a day.
Symbols for the seasons
Alchemy symbols for the different seasons.
References
http://www.22facts.com/spring/
https://www.metoffice.gov.uk/learning/seasons
https://greenwichmeantime.com/longest-day/equinox-solstice-2010-2019/
https://www.timeanddate.com/calendar/aboutseasons.htmlv
https://www.livescience.com/25202-seasons.html
https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/seasons/en/
https://www.britannica.com/science/spring-season
http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/environment_earth_universe/astronomy_space/revision/5/
https://www.britannica.com/science/celestial-equator





















No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.